Home / Publications / E-library page
You are currently logged in as an
Institutional Subscriber.
If you would like to logout,
please click on the button below.
Home / Publications / E-library page
Only AES members and Institutional Journal Subscribers can download
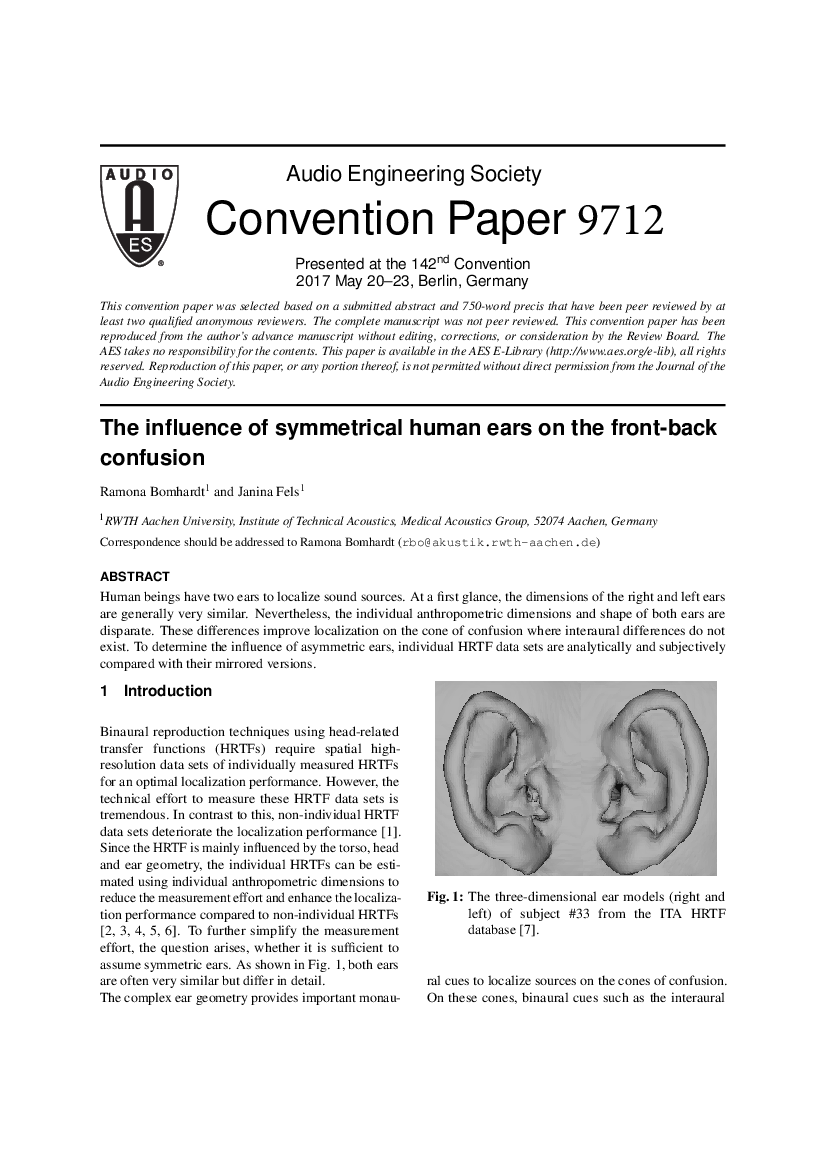
Human beings have two ears to localize sound sources. At a first glance, the dimensions of the right and left ears are generally very similar. Nevertheless, the individual anthropometric dimensions and shape of both ears are disparate. These differences improve localization on the cone of confusion where interaural differences do not exist. To determine the influence of asymmetric ears, individual HRTF data sets are analytically and subjectively compared with their mirrored versions.
Author (s): Bomhardt, Ramona; Fels, Janina
Affiliation:
RWTH Aachen University, Aachen, Germany
(See document for exact affiliation information.)
AES Convention: 142
Paper Number:9712
Publication Date:
2017-05-06
Import into BibTeX
Session subject:
Spatial Audio—Binaural 2
Permalink: https://aes2.org/publications/elibrary-page/?id=18590
(1444KB)
Click to purchase paper as a non-member or login as an AES member. If your company or school subscribes to the E-Library then switch to the institutional version. If you are not an AES member Join the AES. If you need to check your member status, login to the Member Portal.
Bomhardt, Ramona; Fels, Janina; 2017; The Influence of Symmetrical Human Ears on the Front-Back Confusion [PDF]; RWTH Aachen University, Aachen, Germany; Paper 9712; Available from: https://aes2.org/publications/elibrary-page/?id=18590
Bomhardt, Ramona; Fels, Janina; The Influence of Symmetrical Human Ears on the Front-Back Confusion [PDF]; RWTH Aachen University, Aachen, Germany; Paper 9712; 2017 Available: https://aes2.org/publications/elibrary-page/?id=18590